Bootstrap Navbar Button
Overview
Regardless how complex and well-thought web site organization we create, it doesn't mean notably if we fail to give the visitor a comfortable and simple way accessing it and getting to the specific webpage needed quickly and with least efforts no matter the screen size of the device displaying the web site. As soon as it goes to responsive behavior, the navbar can be set up to collapse under a specific screen width and a display horizontal above it looks and user sense. Listed here is how:
Steps to employ the Bootstrap Navbar Button:
Here's things that you require to know before getting started with the navbar:
- Navbars expect a wrapping .navbar with .navbar-toggleable-* to get responsive collapsing as well as coloration classes.
- Navbars and their components are certainly adjustable by default. Utilize optional containers to bound their horizontal width.
- Navbars as well as their elements are set up using flexbox, offering convenient alignment possibilities via utility classes.
- Navbars are simply responsive by default, but you are able to quickly customize them to modify that. Responsive behavior is dependent on Collapse JavaScript plugin.
- Assure availableness utilizing a <nav> component or else, if operating a more general element like a <div>, add in a role="navigation" to every single Bootstrap Navbar Toggle to explicitly identify it just as a milestone area for users of assistive technologies.
Initially we require a <nav> component to cover the entire point up - assign it the . navbar course to begin, a .navbar-fixed-top in order to have it stick at the top of the page in all times or .navbar-fixed-bottom if for a factor you would want it repaired near the bottom. Right here additionally is the place to take care of the whole element's shade-- in Bootstrap 4 you have some brand-new amazing clesses for that like .navbar-dark, .navbar-light or the classes linking the background to the contextual colors in the framework-- like .bg-info, .bg-success and so forth. Naturally typically you might have a predefined color scheme to adhere to - like a brand's shade or something-- after that just add a basic design =" background-color: ~ your color ~" quality or define a bg-* class and assign it to the <nav> element.
Hence the flexible behavior it the point of the Bootstrap framework we'll focus on generating flexible navbars because practically these are actually the ones we'll mainly need.
Statin details this way the next step in creating the navbar is producing a <div> element to keep the whole navbar and its contents and collapse at the desired device size-- assign it the .collapse class and .navbar-toggleable- ~ the largest display size in which you need it collapsed ~ for example - .navbar-toggleable-sm
One other factor to note
A detail to mark is that in the latest Bootstrap 4 framework the ways of selecting the placement of the navbar elements has been altered a bit for different forms to be potentially specified to various screen dimensions. It gets accomplished by the .pull- ~ screen size ~ -left and also .pull- ~ screen size ~ -right classes-- assign them to the .nav element to get the desired placement in the selected size and above it. There also is a .pull- ~ screen size ~ -none removing the positioning if required. These all come to change the old Bootstrap 3 .navbar-right and .navbar-left classes which in the new version are no longer required.
You can at last make a decision to include a basic form part inside your navbar-- usually right after the .nav element. To make it display appropriately you can work with the placement classes discussed above also assigning .form-inline to it. The .navbar-form class the forms required to carry in the old version has been dropped in Bootsrtap 4.
Read on to get an illustration and list of supported sub-components.
As an examples
Sustained content
Navbars featured built-in help for a handful of sub-components. Pick the following as needed:
.navbar-brand for your product line, company, or project name.
.navbar-nav for a full-height as well as light-weight site navigation (including help for dropdowns)..
.navbar-toggler for utilization along with collapse plugin and some other navigation toggling behaviours.
.form-inline for any form controls as well as activities.
.navbar-text for adding vertically focused strings of message.
.collapse.navbar-collapse for organizing and hiding navbar materials through a parent breakpoint.
Here is literally an instance of all the sub-components utilized inside a responsive light-themed navbar which automatically collapses at the md (medium) breakpoint.

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarSupportedContent" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarSupportedContent">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Label
The .navbar-brand may be put on most elements, but an anchor functions best just as certain elements might actually demand utility classes or customized looks.

<!-- As a link -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</nav>
<!-- As a heading -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<h1 class="navbar-brand mb-0">Navbar</h1>
</nav>Bring in illustrations to the .navbar-brand will definitely always require customized formats as well as utilities to correctly dimension. Right here are several good examples to demonstrate.

<!-- Just an image -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">
<div class="img"><img src="/assets/brand/bootstrap-solid.svg" width="30" height="30" alt=""></div>
</a>
</nav>
<!-- Image and text -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">
<div class="img"><img src="/assets/brand/bootstrap-solid.svg" width="30" height="30" class="d-inline-block align-top" alt=""></div>
Bootstrap
</a>
</nav>Nav
Navbar navigating web links based on .nav solutions along with their very own modifier class and need utilize toggler classes for appropriate responsive styling . Site navigation in navbars will as well progress to possess as much horizontal space as available to keep your navbar elements completely lined up.
Active conditions-- with .active-- to signify the recent webpage can be applied directly to .nav-link-s or their immediate parent .nav-item-s.
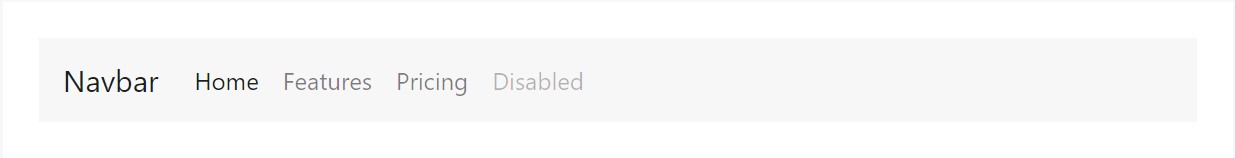
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNav" aria-controls="navbarNav" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNav">
<ul class="navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>And due to the fact that we use classes for our navs, you have the ability to keep away from the list-based approach totally if you prefer.
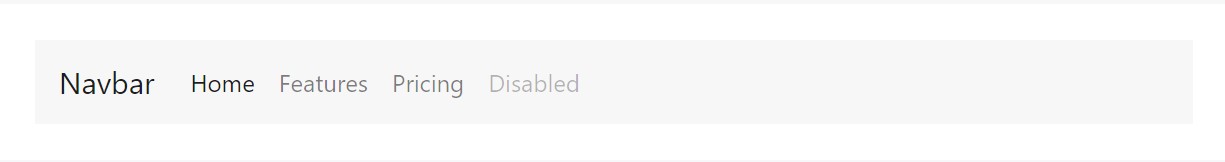
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNavAltMarkup" aria-controls="navbarNavAltMarkup" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
<a class="nav-item nav-link active" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</div>
</div>
</nav>You may as well implement dropdowns in your navbar nav. Dropdown menus need a covering component for placing, thus ensure to use embedded and separate elements for .nav-item and .nav-link just as displayed below.
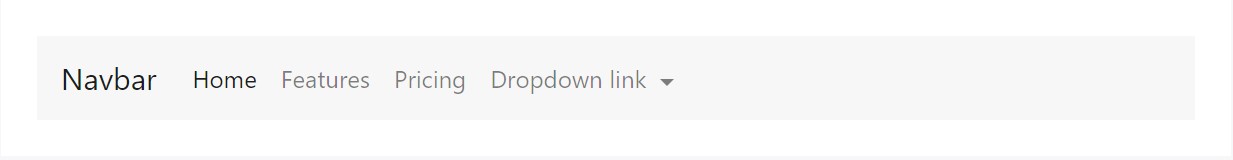
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNavDropdown" aria-controls="navbarNavDropdown" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavDropdown">
<ul class="navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item dropdown">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href="http://example.com" id="navbarDropdownMenuLink" data-toggle="dropdown" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false">
Dropdown link
</a>
<div class="dropdown-menu" aria-labelledby="navbarDropdownMenuLink">
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Action</a>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Another action</a>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Something else here</a>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>Forms
Place various form controls and elements inside a navbar through .form-inline.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</nav>Straighten the contents of your inline forms with utilities as required.
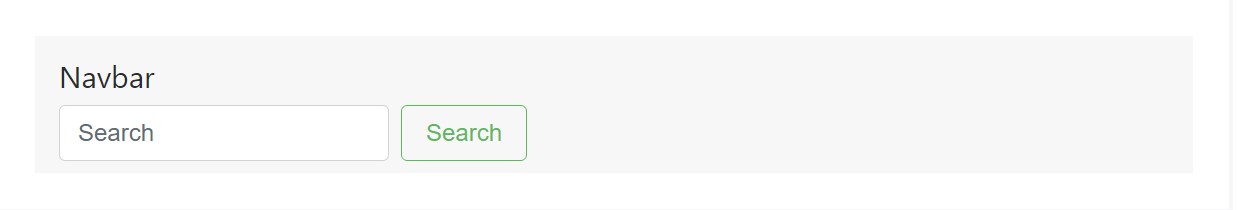
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded justify-content-between">
<a class="navbar-brand">Navbar</a>
<form class="form-inline">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</nav>Input groups operate, too:

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-addon" id="basic-addon1">@</span>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" aria-describedby="basic-addon1">
</div>
</form>
</nav>Several buttons are sustained as component of these navbar forms, too. This is also a terrific reminder that vertical positioning utilities can be utilized to adjust several sized elements.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success" type="button">Main button</button>
<button class="btn btn-sm align-middle btn-outline-secondary" type="button">Smaller button</button>
</form>
</nav>Text message
Navbars can incorporate bits of text message with .navbar-text. This particular class sets vertical placement and horizontal spacing for strings of message.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<span class="navbar-text">
Navbar text with an inline element
</span>
</nav>Mix and matchup with additional components and utilities like wanted.
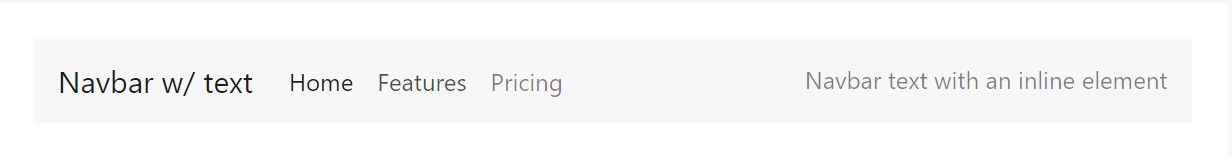
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarText" aria-controls="navbarText" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar w/ text</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarText">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
</ul>
<span class="navbar-text">
Navbar text with an inline element
</span>
</div>
</nav>Color pattern
Theming the navbar has certainly never been simpler because of the combination of style classes and background-color utilities. Pick from .navbar-light for use with light background color options , alternatively .navbar-inverse for dark background color options. After that, modify with .bg-* utilities.
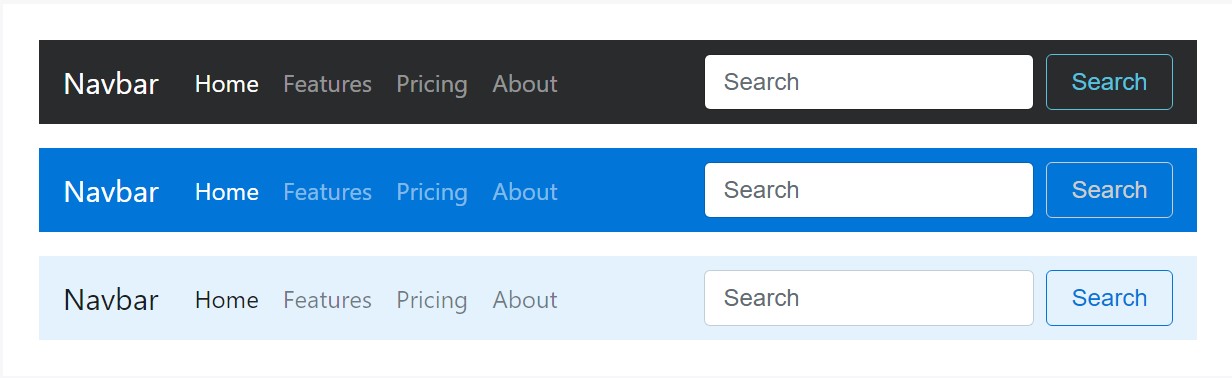
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-inverse">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-primary">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>
<nav class="navbar navbar-light" style="background-color: #e3f2fd;">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>Containers
Although it is simply not needed, you are able to wrap a navbar in a .container to centralize it on a webpage or provide one just within to simply center the materials of a corrected or else static top navbar.

<div class="container">
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</nav>
</div>As the container is inside of your navbar, its horizontal padding is gotten rid of at breakpoints beneath your defined
.navbar-toggleable-* class. This makes sure that we are certainly not doubling up on padding uselessly on lower viewports whenever your navbar is collapsed.

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</div>
</nav>Placement
Employ placement utilities to insert navbars inside non-static places. Go with set to the top, set to the bottom, or stickied to the top . Note that position: sticky, used for .sticky-top, really isn't fully carried in every web browser.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Full width</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar fixed-top navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Fixed top</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar fixed-bottom navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Fixed bottom</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar sticky-top navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Sticky top</a>
</nav>Responsive activities
Navbars has the ability to incorporate .navbar-toggler, .navbar-collapse, and .navbar-toggleable-* classes to alter when their content collapses behind a button . In union with some other utilities, you can efficiently pick when to demonstrate or cover specific components.
Toggler
Navbar togglers can be left or right coordinated having .navbar-toggler-left or .navbar-toggler-right modifiers. These are absolutely set up inside of the navbar to avoid intrusion with the collapsed state. You have the ability to additionally use your personal formats to set togglers. Listed here are good examples of different toggle designs.
Without .navbar-brand presented in lowest breakpoint:

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarTogglerDemo01" aria-controls="navbarTogglerDemo01" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarTogglerDemo01">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Hidden brand</a>
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto mt-2 mt-lg-0">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Together with a brand name displayed on the left and toggler on the right:

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarTogglerDemo02" aria-controls="navbarTogglerDemo02" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarTogglerDemo02">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto mt-2 mt-md-0">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Alternative content
In certain cases you really want to operate the collapse plugin to trigger hidden material someplace else on the web page. Considering that plugin works with the id and data-target matching, that is really conveniently carried out!

<div class="pos-f-t">
<div class="collapse" id="navbarToggleExternalContent">
<div class="bg-inverse p-4">
<h4 class="text-white">Collapsed content</h4>
<span class="text-muted">Toggleable via the navbar brand.</span>
</div>
</div>
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-inverse">
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarToggleExternalContent" aria-controls="navbarToggleExternalContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
</nav>
</div>Final thoughts
So basically these are the way a navbar should be constructed in Bootstrap 4 and the fresh cool modifications arriving with the newest version. All that's left for you is thinking of as cool page structure and content.
Inspect some on-line video tutorials regarding Bootstrap Navbar:
Connected topics:
Bootstrap Navbar formal records
Line up navbar object to the right within Bootstrap 4 alpha 6
Bootstrap Responsive menu within Mobirise
CSS3 Bootstrap Accordion Menu Compilation
JavaScript Bootstrap Collapse Menu Templates