Bootstrap Breakpoints Using
Intro
Getting in consideration all the realizable screen widths in which our internet pages could eventually showcase it is important to compose them in a method giving undisputed clear and strong visual appeal-- normally applying the assistance of a powerful responsive framework like easily the most well-known one-- the Bootstrap framework in which most current edition is currently 4 alpha 6. But what it actually performs to assist the pages pop in fantastic on any display screen-- why don't we take a look and observe.
The major standard in Bootstrap ordinarily is putting certain ordination in the countless feasible device screen widths ( or else viewports) putting them into a few variations and styling/rearranging the information properly. These are also termed grid tiers or else display scales and have developed quite a little through the different versions of the most famous currently responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4.
Efficient ways to work with the Bootstrap Breakpoints Default:
Commonly the media queries get determined with the following structure @media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~. The requirements can easily limit one end of the interval like min-width: 768px of each of them like min-width: 768px - while the viewport size in within or equivalent to the values in the requirements the rule employs. Since media queries belong to the CSS language there certainly may be a lot more than one query for a single viewport size-- if so the one particular being reviewed by browser last has the word-- the same as regular CSS rules.
Varieties of Bootstrap versions
Within Bootstrap 4 compared to its predecessor there are 5 display widths however because recent alpha 6 build-- simply 4 media query groups-- we'll return to this in just a sec. As you most probably realize a .row within bootstrap features column features maintaining the actual web page material which in turn have the ability to extend up to 12/12's of the detectable width accessible-- this is simplifying yet it's one more thing we're discussing here. Each and every column component get determined by one of the column classes including .col - for column, display scale infixes defining down to what display scale the material will remain inline and will cover the whole horizontal width below and a number demonstrating how many columns will the element span when in its display size or just above.
Display screen sizes
The screen scales in Bootstrap normally utilize the min-width requirement and come as follows:
Extra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like col-6 - such element for example will span half width no matter the viewport.
Extra small-- widths less than 576px-- This screen actually does not feature a media query still the designing for it instead gets utilized just as a usual rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths just above. What's likewise brand-new within Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it really doesn't utilize any type of scale infix-- so the column design classes for this kind of screen scale get defined like col-6 - this sort of element for instance will span half width despite the viewport.
Small screens-- uses @media (min-width: 576px) ... and the -sm- infix. { For example element coming with .col-sm-6 class will certainly cover half size on viewports 576px and larger and full width below.
Medium display screens-- uses @media (min-width: 768px) ... and also the -md- infix. As an example component possessing .col-md-6 class is going to extend half size on viewports 768px and wider and entire size below-- you've undoubtedly got the practice already.
Large screens - works with @media (min-width: 992px) ... and the -lg- infix.
And lastly-- extra-large displays - @media (min-width: 1200px) ...-- the infix here is -xl-
Responsive breakpoints
Given that Bootstrap is designed to be mobile first, we employ a number of media queries to establish sensible breakpoints for designs and user interfaces . These kinds of Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid are usually built upon minimal viewport sizes and help us to size up factors when the viewport changes.
Bootstrap primarily applies the following media query stretches-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass files for design, grid system, and components.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...As we formulate source CSS in Sass, each media queries are simply obtainable by Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We occasionally work with media queries which perform in the other course (the offered screen dimension or smaller sized):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce again, these types of media queries are also available through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for aim a specific section of screen sizes using the minimum and highest Bootstrap Breakpoints Using widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Such media queries are in addition obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Likewise, media queries may cover various breakpoint widths:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for targeting the equivalent display screen dimension range would definitely be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Conclusions
In addition to defining the size of the webpage's features the media queries occur all around the Bootstrap framework usually getting identified by means of it - ~screen size ~ infixes. When seen in several classes they ought to be interpreted just like-- regardless of what this class is handling it is generally accomplishing it down to the display width they are referring.
Check out a couple of video short training relating to Bootstrap breakpoints:
Related topics:
Bootstrap breakpoints formal documents"

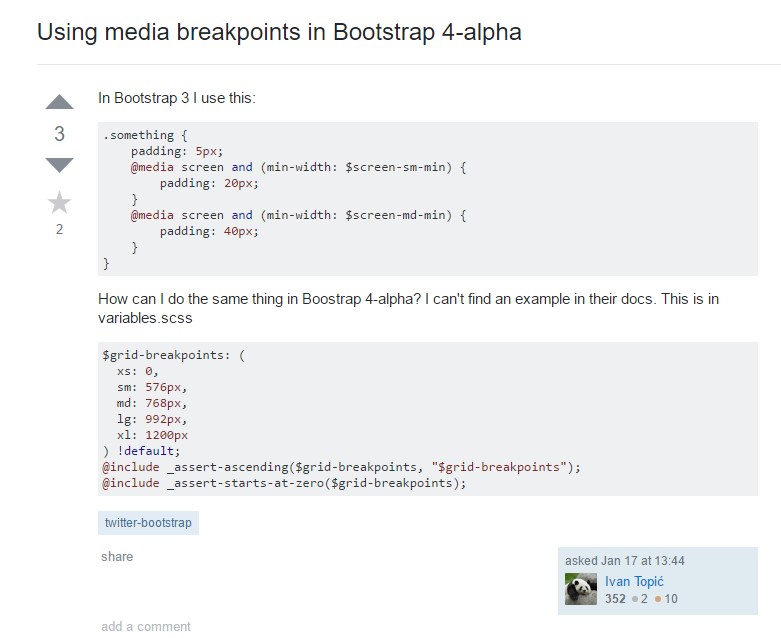
Bootstrap Breakpoints difficulty
Change media query breakpoint units from em to px